PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
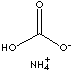
H.S. CODE
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES (60% Solution))
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet
Local:
Pure ammonium bisulfite is a white crystalline solid.
Commercially, however, aqueous liquid form (typically
60%) is common. Ammonium bisulfite's
reductive and sulfonating properties provide versatile
applications. It is used as an oxygen scavenger to eliminate the
dissolved oxygen in waste water and in pipes. Ammonium bisulfite is a reductive bleaching
agent. It reduces carbonyl and alcohol groups, which function as colorants of
the substances. It is used in bleaching mechanical paper pulp, cotton, wool and
kaolin clay. Additional applications include as a preservative (antioxidant)
and a hair waving agent. Ammonium bisulfite is used in industries concerned with leather
processing, food and beverage
processing, gas purification, water treatment
to remove excess chlorine,
textiles
and pulp
processing, and many others.
It is used as a reducing agent in
chemical manufacturing. It is an alternative to sulfur dioxide which is
used in sterlization of equipment.
60% AQ. SOLUTION
ASSAY
59.0 - 61.0%
1.31 - 1.35
pH
4.5 - 5.5
TRANSPORTATION
OTHER INFORMATION
Sulfate (also spelled sulphate in Europe) is any chemical compound containing the SO42- ion related to sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Sulfates are salts or esters of sulfuric acid, formed by replacing one or both of the hydrogens with a metal or a radical as in sodium sulfate, Na2SO4. Sulfates in which both hydrogens are replaced are called normal sulfates. Bisulfate is a compound that has the HSO4- radical. Bisulfate (called also hydrogen sulfate or acid sulfate) is a compound formed by replacing only one hydrogen in sulfuric acid. Sulfite (also sulphite) is a compound that contain the sulfite ion SO32-. Sulfites are salts or esters of sulfurous acid (H2SO3), formed by replacing one or both of the hydrogens with a metal or a radical as in sodium sulfite, Na2SO3. Sulfites in which both hydrogens are replaced are called normal sulfites. Bisulfite is a compound that has the HSO3- radical. Bisulfate (called also hydrogen sulfite or acid sulfite) is a compound formed by replacing only one hydrogen in sulfurous acid. The term of 'meta' or 'pyro' is the chemical prefix for oxo acid formed through the loss of one water molecule (dehydration) from two molecules of ortho acid by heating. Pyrosulfuric acid is an example ( 2H2SO4 - H2O = H2S2O7). Ortho acid is the compound fully hydrated acid or its salts. Orthophosphoric acid is an example (2·H3PO4 = P2O5.3H2O), in contrast to the less hydrated form, pyrophosphoric acid (2·HPO3 = P2O5.H2O). Na2O5S2 is called sodium metabisulfite (2·HNaO3S - H2O). Sulfide is a compound having one or more sulfur atoms in which the sulfur is connected directly to a carbon, metal, or other nonoxygen atom; for example sodium sulfide, Na2S. Sulfide ion is S2- with oxidation number -2. Bisulfide ion is an anion formed by two sulfur atoms having an overall -2 charge, (S2)2-. Sulfamate is a salt of sulfamic acid (HSO3NH2). Calcium sulfamate Ca(SO3NH2)2 is an example.